
Introduction
Life insurance has long been recognized as a useful way to provide for your heirs and loved ones when you die. While naming your policy’s beneficiaries should be a relatively simple task, there are a number of situations that can easily lead to unintended and adverse consequences. Here are several life insurance beneficiary traps you may want to discuss with a professional.

Not naming a beneficiary
The most obvious mistake you can make is failing to name a beneficiary of your life insurance policy. But simply naming your spouse or child as beneficiary may not suffice. It is conceivable that you and your spouse could die together or that your named beneficiary may die before you and you haven’t named successor beneficiaries. If the beneficiaries you designated are not living at your death, the insurance company may pay the death proceeds to your estate, which can lead to other potential problems.
Death benefit paid to your estate
If your life insurance is paid to your estate, several undesired issues may arise. First, the insurance proceeds likely become subject to probate, which may delay the payments to your heirs. Second, life insurance that is part of your probate estate is subject to claims of your probate creditors. Not only might your heirs have to wait to receive their share of the insurance, but your creditors may satisfy their claims out of those proceeds first.

Naming a minor child as beneficiary
Insurance companies will rarely pay life insurance proceeds directly to a minor. Typically, the court appoints a guardian — a potentially costly and time-consuming process — to handle the proceeds until the minor beneficiary reaches the age of majority according to state law. If you want the life insurance proceeds to be paid for the benefit of a minor, you may consider creating a trust that names the minor as beneficiary. Then the trust manages and pays the proceeds from the insurance according to the terms and conditions you set out in the trust document. Consult with an estate attorney to decide on the course that works best for your situation.
Disqualifying a beneficiary from government assistance
A beneficiary you name to receive your life insurance may be receiving or be eligible to receive government assistance due to a disability or other special circumstance. Eligibility for government benefits is often tied to the financial circumstances of the recipient. The payment of insurance proceeds may be a financial windfall that disqualifies your beneficiary from eligibility for government benefits, or the proceeds may have to be paid to a government entity as reimbursement for benefits paid. Again, an estate attorney can help you address this issue.
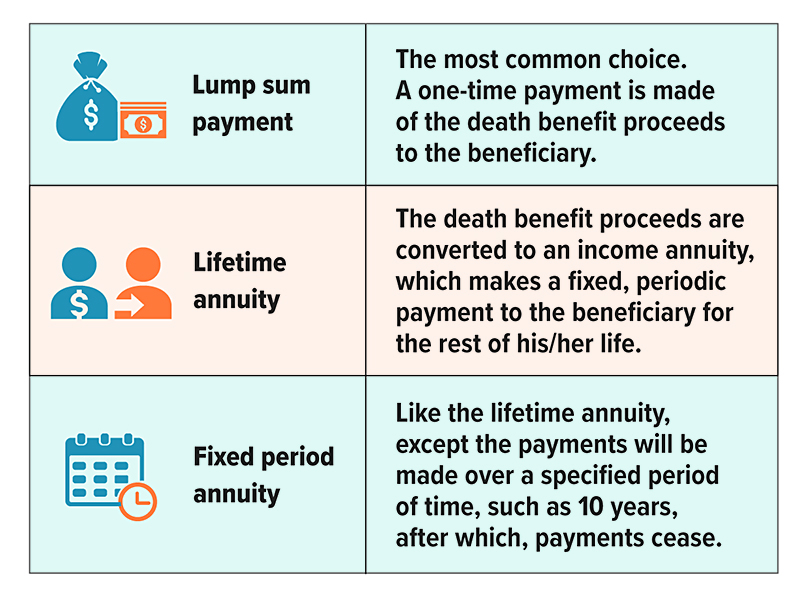
Life Insurance Payout Options
Most life insurance policies offer several options to the policy beneficiary, including:
Creating a taxable situation
Generally, life insurance death proceeds are not taxed when they’re paid. However, there are exceptions to this rule, and the most common situation involves having three different people as policy owner, insured, and beneficiary. Typically, the policy owner and the insured are one and the same person. But sometimes the owner is not the insured or the beneficiary. For example, mom may be the policy owner on the life of dad for the benefit of their children. In this situation, mom is effectively creating a gift of the insurance proceeds for her children/beneficiaries. As the donor, mom may be subject to gift tax. Consult a financial or tax professional to figure out the best way to structure the policy.

As with most financial decisions, there are expenses associated with the purchase of life insurance. Policies commonly have mortality and expense charges. In addition, if a policy is surrendered prematurely, there may be surrender charges and income tax implications. The cost and availability of life insurance depend on factors such as age, health, and the type and amount of insurance purchased.

While trusts offer numerous advantages, they incur up-front costs and often have ongoing administrative fees. The use of trusts involves a complex web of tax rules and regulations. You should consider the counsel of an experienced estate planning professional and your legal and tax advisors before implementing such strategies.
This content has been reviewed by FINRA.
